In recent years, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has had a huge impact on our daily lives like never before. Day after day, we see products that automate several tasks and serve us in an intelligent way. The proposed solutions of AI are rather personalized than standard. Today we find AI everywhere in large and small industries. Giant companies like Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Apple, Samsung, etc… spent millions of dollars in AI research to improve their products.
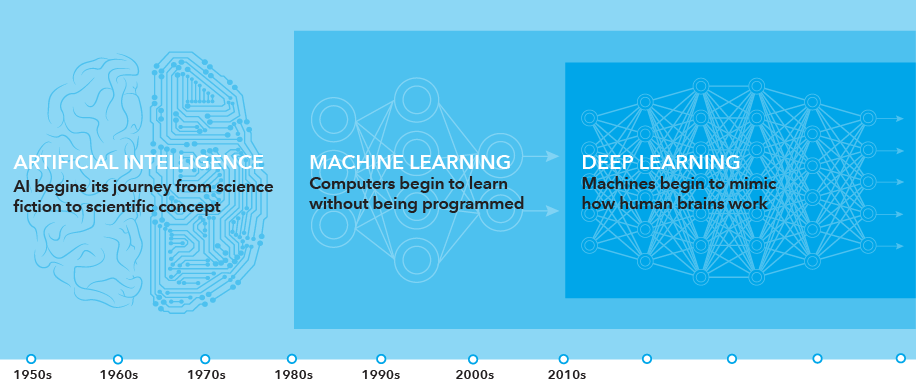
At a more professional level, when we talk about AI, we use the terms “Machine Learning” and “Deep Learning”. So, we need to define clearly what we are talking about when we mention AI .
What are Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning? How do they relate to each other?
Artficial Intelligence (AI)
According to the father of Artificial Intelligence, John McCarthy, it is
The science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs.
Artificial Intelligence is a way of making a computer, a computer-controlled robot, or a software think intelligently, in the similar manner the intelligent humans think.
The central goal of AI is to provide a set of algorithms and techniques that can be used to solve problems that humans perform intuitively and near automatically, but are otherwise very challenging for computers.
In the past decade, AI has given us self-driving cars, practical speech recognition, effective web search, and a vastly improved understanding of the human genome.
AI is so pervasive today that you probably use it dozens of times a day without knowing it. Many researchers also think it is the best way to make progress towards human-level intelligence.
Among the main classes of artificial intelligence is machine learning and deep learning.
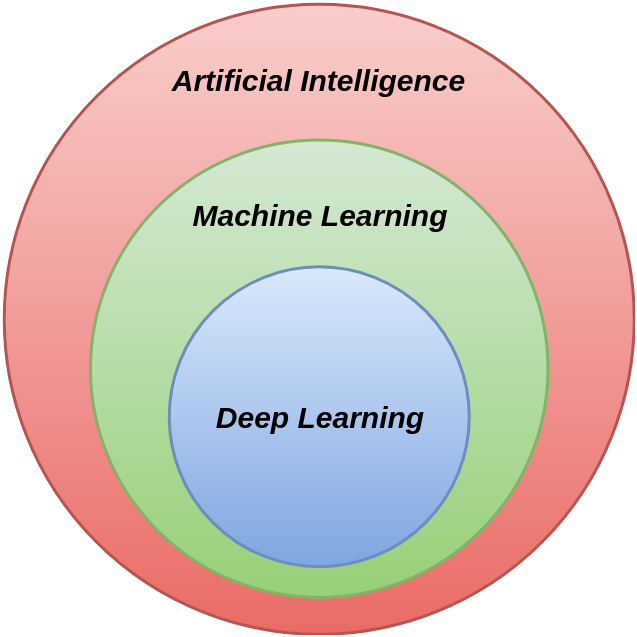
A Venn diagram describing deep learning as a subfield of machine learning which is in turn a subfield of artificial intelligence.
Machine Learning (ML)
Here’s a basic definition of machine learning:
Algorithms that parse data, learn from that data, and then apply what they’ve learned to make informed decisions
Machine learning is the science of getting computers to act without being explicitly programmed. Although machine learning is a field within computer science, it differs from traditional computational approaches. In traditional computing, algorithms are sets of explicitly programmed instructions used by computers to calculate or problem solve. Machine learning algorithms instead allow for computers to train on data inputs and use statistical analysis in order to output values that fall within a specific range. Because of this, machine learning facilitates computers in building models from sample data in order to automate decision-making processes based on data inputs.
Any technology user today has benefitted from machine learning. Facial recognition technology allows social media platforms to help users tag and share photos of friends. Optical character recognition (OCR) technology converts images of text into movable type. Recommendation engines, powered by machine learning, suggest what movies or television shows to watch next based on user preferences. Self-driving cars that rely on machine learning to navigate may soon be available to consumers.
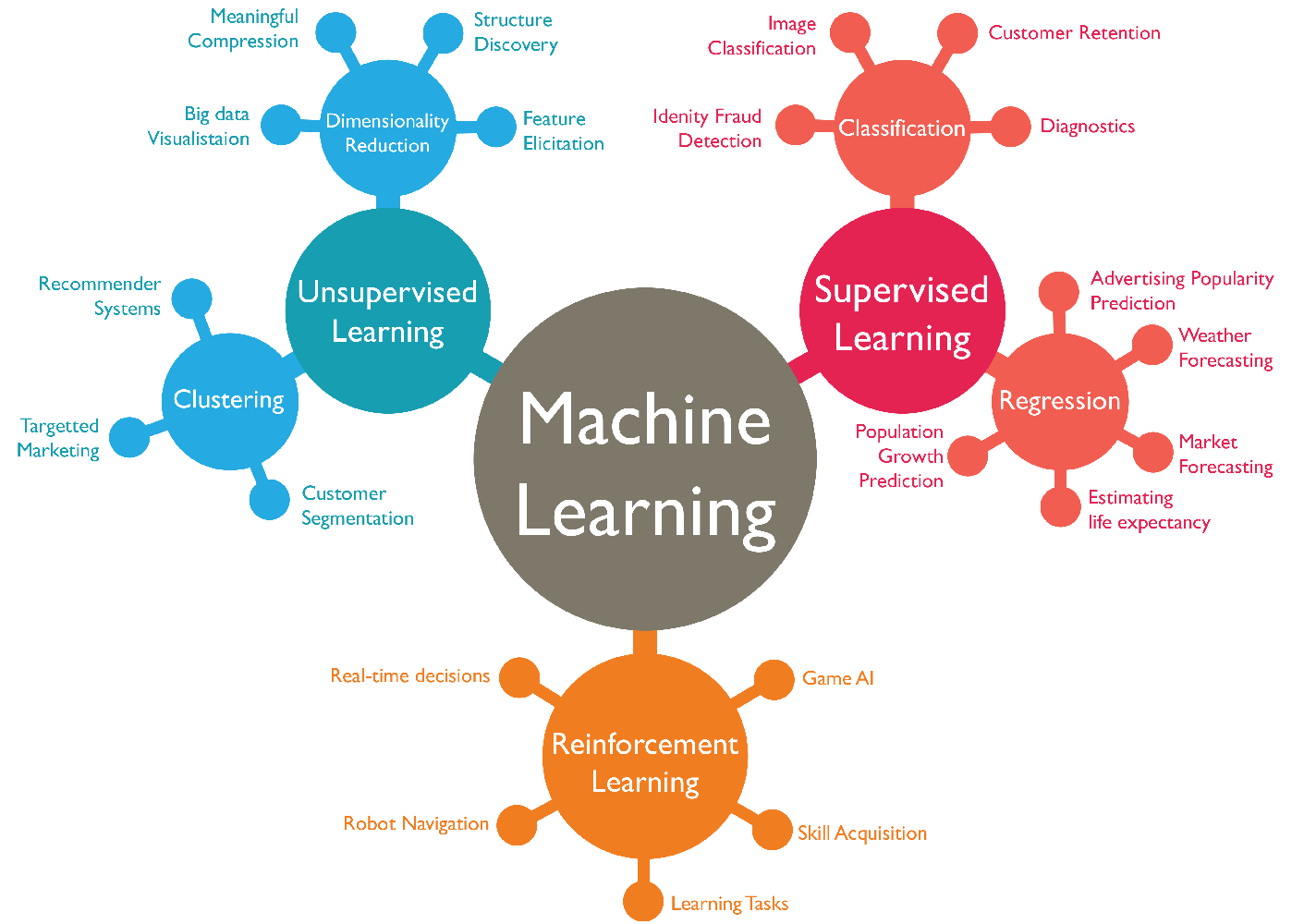
Two of the most widely adopted machine learning methods are supervised learning which trains algorithms based on example input and output data that is labeled by humans, and unsupervised learning which provides the algorithm with no labeled data in order to allow it to find structure within its input data.
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep learning is a subfield of machine learning, which is, in turn, a subfield of artificial intelligence.
The history of neural networks and deep learning is a long, somewhat confusing one. It may surprise you to know that “deep learning” has existed since the 1940s undergoing various name changes, including cybernetics, connectionism, and the most familiar, Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs).
The first neural network model came from McCulloch and Pitts in 1943. Then, in the 1950s the seminal Perceptron algorithm was published by Rosenblatt. This model could automatically learn the weights required to classify an input (no human intervention required).
Today, the latest incarnation of neural networks as we know it is called deep learning. What sets deep learning apart from its previous incarnations is that we have faster, specialized hardware with more available training data.
